MySQL
This page provides information for connecting your application to your MySQL database and for using queries to manage its content.
Appsmith supports MySQL versions 5.5, 5.6, 5.7, and 8.0.
Connect MySQL
To connect to MySQL, you should whitelist the IP address of the Appsmith deployment 18.223.74.85 and 3.131.104.27 on your database instance or VPC before connecting to the database.
Connection parameters
The following section is a reference guide that provides a complete description of all the parameters to connect to a MySQL database.
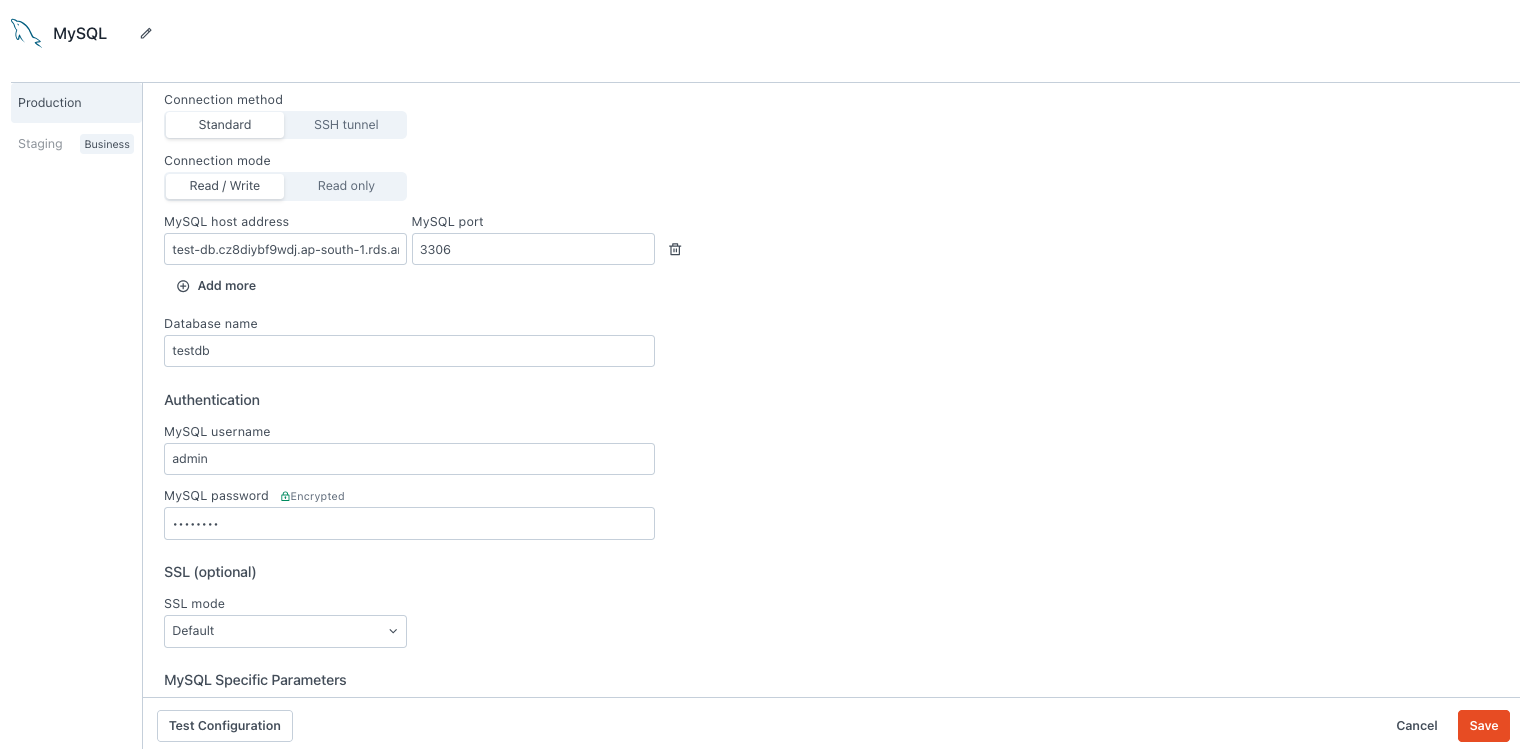
Connection method
- Standard: Connect to the database using host address, username and password. Use this method if the MySQL database is directly accessible at an IP address or if you are unsure of which method to use.
- SSH tunnel: Connect over an SSH connection. This allows you to connect to a database instance which is hidden or secured behind an SSH server.
Connection mode
- Read Only: Gives Appsmith read-only permission on the database. Use this mode when you only need to fetch records, not write them.
- Read / Write: Gives Appsmith both read and write permissions on the database. This allows you to make changes to your data via all CRUD queries.
MySQL host address
MySQL port
3306 by default if you do not specify one.Database name
MySQL username
MySQL password
SSH host address
SSH port
22 by default if left empty. SSH username
SSH Key
SSL mode
- Default: SSL is used if the server supports it.
- Required: The connection is rejected if SSL isn't available.
- Disabled: Disallows all administrative requests over HTTPS. It uses a plain unencrypted connection.
Server Timezone Override
UTC) to use for your queries.Create queries
The following section provides examples of creating basic CRUD queries for MySQL.
MySQL databases are queried using standard SQL syntax. For a language reference, see MySQL's Language Structure.
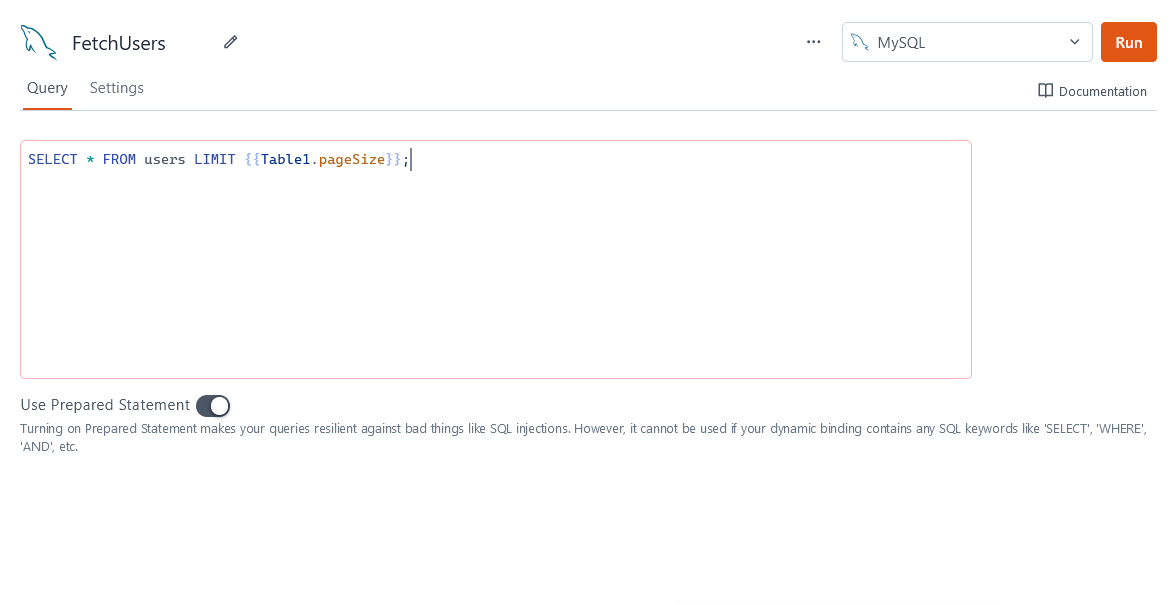
Fetch data
SELECT * FROM users LIMIT {{ UsersTable.pageSize }} OFFSET {{ UsersTable.pageOffset }};
In the above example, UsersTable is the name of the Table widget used to display the data using server-side pagination to control how much data is queried at once.
Insert data
INSERT INTO users
(name, gender, email)
VALUES
(
{{ NameInput.text }},
{{ GenderDropdown.selectedOptionValue }},
{{ EmailInput.text }}
);
In the above example, NameInput, GenderDropdown, and EmailInput are the names of the widgets used to capture input from the user for name, gender, and email fields, respectively.
Update data
UPDATE users
SET email = {{ EmailInput.text }}
WHERE id = {{ UsersTable.selectedRow.id }};
In the above example, EmailInput is the name of the Input widget used to capture the email entered by the user. UsersTable is the Table widget where the user selects the row to update the user's email.
Delete data
DELETE FROM users WHERE id = {{ UsersTable.selectedRow.id }};
In the above example, UsersTable is the name of the Table widget where the user selects the row for deletion.
Prepared statements are turned on by default in your queries to help prevent SQL injection attacks. For more details, see Prepared Statements.
SQL modes
SQL_MODE is a system variable in MySQL that can:
- Configure the server's strictness when accepting input data,
- Adjust syntax to conform more closely to standard SQL,
- Provide better compatibility with other databases.
In particular, strict mode can help you ensure the integrity of your data by preventing the database from automatically inserting default values for missing or invalid data.
For more information, see the docs for MySQL's SQL Modes.
Troubleshooting
If you are experiencing difficulties, you can refer to the Datasource troubleshooting guide or the MySQL Errors page, or contact the support team using the chat widget at the bottom right of this page.
